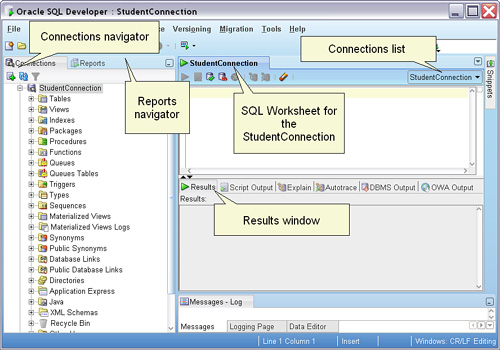
4 SQL Developer Introduction
4.1 Introduction
This module introduces Oracle SQL Developer, demonstrates how to work within the SQL Worksheet, and outlines techniques for exporting data in user-friendly formats such as Excel and CSV. It also touches on considerations when working with large datasets.
4.2 SQL Developer Overview
4.2.1 What is SQL Developer?
SQL Developer is a graphical interface for running SQL queries, managing database connections, and visualizing data outputs. It is a tool that allows users like you to interact with an Oracle database server.
In Oracle’s client-server architecture, the database is divided into two parts: the client and the server.
- Client: This is where SQL Developer runs. It is the front-end application that users interact with to send requests to the database.
- Server: This is where the Oracle database resides. It processes the requests from the client, manages data, and sends the results back to the client.
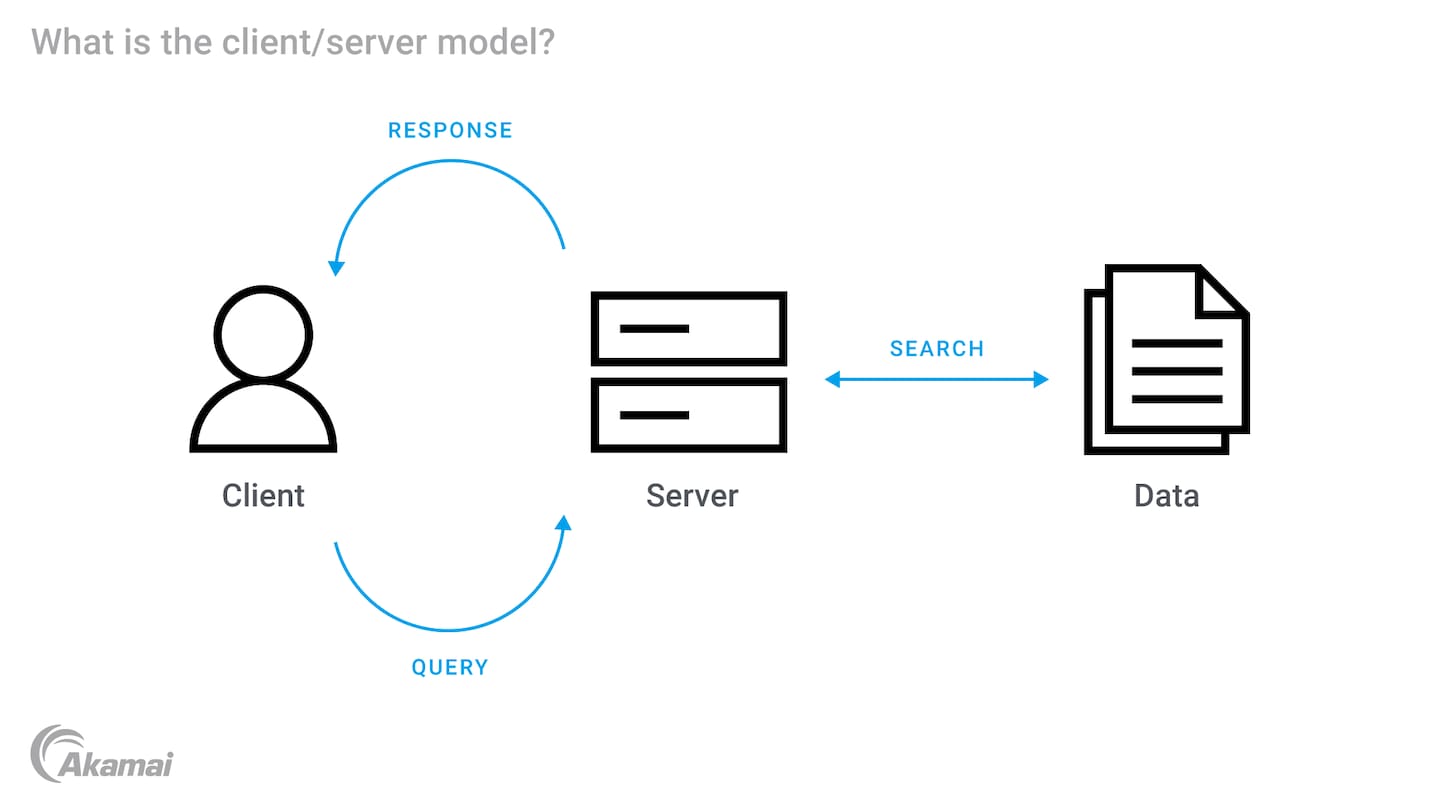
SQL Developer (the client) allows you to send queries and commands to the Oracle database (the server), which processes these commands and returns the results to SQL Developer for you to see and use.
4.2.2 Key Application Concepts
Here, we will quickly discuss the main components which comprise SQL Developer.
SQL Worksheet
You can open a worksheet by:
- Clicking the SQL Worksheet icon in the toolbar.
- Right-clicking a connection name and choosing Open SQL Worksheet.
- Using the Tools > SQL Worksheet menu option.
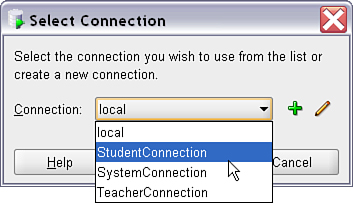
Connections
Each worksheet tab is tied to a specific database connection. You can:
- Open multiple worksheets per connection.
- Use the Connections list to switch execution contexts.
Executing SQL
- Enter SQL in the worksheet and click the green triangle (or press F9) to execute.
- The Results tab will display returned data with row numbers (for display only) and column headers.

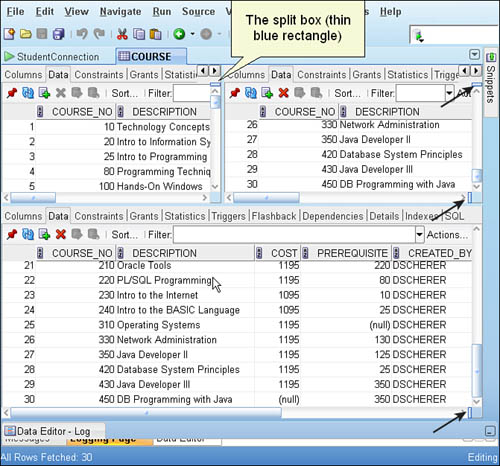
Vertical and Horizontal Splits
You can split your SQL Worksheet or query result tabs either horizontally (top/bottom) or vertically (side-by-side). This is especially helpful when:
- Editing different parts of a large script
- Comparing two separate queries
- Viewing query results in one pane while editing SQL in another
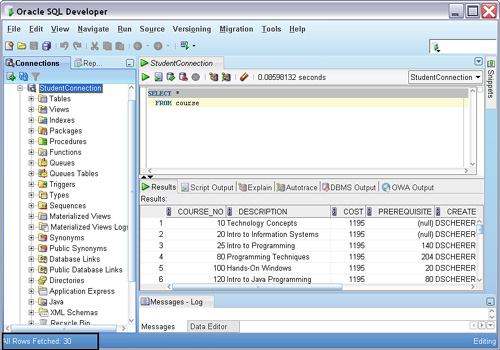
Results Grid
The grid displays query results, which can be:
- Copied to the clipboard.
- Exported to various formats (Excel, CSV, etc.).
- Filtered or sorted by clicking on column headers.
4.3 Exporting to Excel and CSV Formats
SQL Developer supports data exports from both the Data tab and the Results grid.
4.3.1 Steps For Data Export
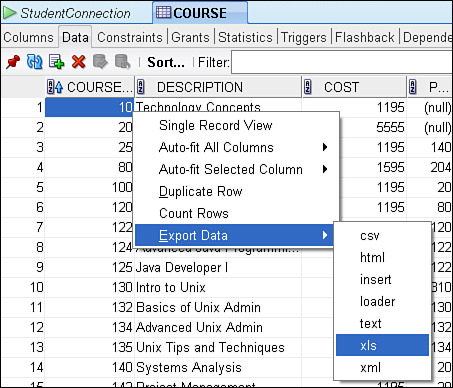
Right-click on any data grid and choose Export.
Alternatively, use Actions > Export from the menu.
Choose a format:
- Excel (.xlsx)
- CSV
- HTML
- SQL INSERT statements
- SQL*Loader (.ldr)
4.3.2 Large Dataset Considerations
Be cautious when exporting large datasets, as they can lead to performance issues or timeouts. Here are some strategies to manage large exports effectively:
Avoid SELECT * When dealing with large tables. Select only needed columns and/or rows.
Limit Rows: Use the Rows to Fetch option in the export dialog to limit the number of rows returned.
Filtering: Use WHERE or FETCH FIRST N ROWS ONLY statements or the Columns/Where export tabs to reduce volume.